Researchers at the School of Economics are committed to public engagement in their research activities. This includes communicating research findings to the wider public, engaging with policy-makers and other stakeholders in developing their research and disseminating findings, and serving in positions outside of academia where their research expertise can provide a unique perspective on economic and social issues. This page documents some of the research staff’s public engagement activities and ongoing research projects with a goal of wider impact.
Agricultural policy for small-holder farms

The capacity of governments to formulate effective agricultural policy aimed at small and family farms is often constrained by market failures, especially in countries marked by poverty and underdevelopment. Sophia Davidova is presently engaged in work for the United Nations Food and Agricultural Organisation to develop the capacity of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Rural Affairs (MAFRD) in Kosovo to improve commercialisation of small and family farmers. A planned workshop at the School of Economics will focus on policy recommendations to rebalance agricultural policy in Kosovo with participation of high level officials from MAFRD and FAO. The research underpinning the impact include output of collaborative EU projects focused on the Common Agricultural Policy, semi-subsistence farms and the functioning of labour market, as well as research on small farms in different development contexts.
Early marriage
 Large numbers of women in poor countries marry in their adolescence because of poverty or long-standing customs, with adverse consequences for their health, education and labour force participation. Using theoretical models of marriage markets and micro-level data, Zaki Wahhaj is investigating the causes and consequences of early marriage in developing countries. This work is funded by Australian Aid and conducted in collaboration with researchers at the University of Malaya and Brac University in Bangladesh. Amrit Amirapu and Zaki Wahhaj are investigating whether and to what extent formal legal institutions can shape early marriage practices and attitudes towards them in a project funded by the UK Department for International Development’s EDI Research Programme. These projects seek to inform recent efforts by international development agencies and national governments to develop programmes and introduce legislation to address the issue of child marriage. Further details about the projects can be found at http://www.integgra.org/
Large numbers of women in poor countries marry in their adolescence because of poverty or long-standing customs, with adverse consequences for their health, education and labour force participation. Using theoretical models of marriage markets and micro-level data, Zaki Wahhaj is investigating the causes and consequences of early marriage in developing countries. This work is funded by Australian Aid and conducted in collaboration with researchers at the University of Malaya and Brac University in Bangladesh. Amrit Amirapu and Zaki Wahhaj are investigating whether and to what extent formal legal institutions can shape early marriage practices and attitudes towards them in a project funded by the UK Department for International Development’s EDI Research Programme. These projects seek to inform recent efforts by international development agencies and national governments to develop programmes and introduce legislation to address the issue of child marriage. Further details about the projects can be found at http://www.integgra.org/
Export control of dual-use goods
Dual-use goods are those that can be used both for civilian and military purposes. The regulation of international trade in these goods is a key issue in the security agenda of the European Union countries and other exporters of these goods. María García-Alonso‘s research has analysed the strategic aspects of export controls on dual use goods. She is a member of the Chaudfontaine Group, a multidisciplinary group, funded by the European Commission, that brings together European researchers, policymakers and stakeholders from industry to consider ways and means to regulate the trade of dual-use items and technologies. Together with members of the Chaudfontaine Group (led by Professor Quentil Michel from Université de Liège), María is engaged in a European Commission framework contract to provide its Joint Research Centre with technical and academic expertise on strategic trade control, including preparation of training material and delivery of training.
Outbreak of disease in plants and animals
An outbreak of disease in plants or animals can have important economic, social and environmental consequences, and efficient risk management policies depend on a solid understanding of the potential costs and trade-offs associated with alternative policy responses. Based on his extensive research on these issues, Rob Fraser is helping the UK Government’s Science Advisory Council Subgroup on Exotic Diseases to develop a framework for quickly assessing the economic impacts of such outbreaks, with the aim of improving both the effectiveness and timeliness of different policy options. With the UK’s international trading patterns likely to change considerably post-Brexit, the potential benefits of such improvements in disease evaluation techniques is substantial.
Resource misallocation and economic growth

There is growing evidence that potential investments with high economic returns often go unrealised in developing countries. This phenomenon can lead to significant misallocation of resources in the wider economy and impede growth and catch up with advanced economies in the long run. In research for the Asian Development Bank’s Asian Development Outlook, Miguel León-Ledesma uses data from nearly 22,000 firms in 62 countries to investigate the extent of resource misallocation and the factors behind it. Findings have highlighted how institutional weaknesses – associated with trade regulations, functioning of courts, access to finance, political instability, labour regulations, access to infrastructure – are responsible for significant misallocation of resources both within and between countries.
Return migration
Matloob Piracha‘s research explores different facets of migration, including the behaviour and impact of remittances as well as the impact of occupational choice of return migrants. Return migration is an important element in the debate about migration policies. There are a number of countries which were net migrant sending countries less than 10 years ago but are becoming net immigration countries, partly because of the return of its diaspora from abroad. Through the IZA World of Labour project, this research has provided policy-makers in sending and receiving countries with a better understanding of the return phenomenon and help form policies that could be implemented to assist migrants resettle in their home country and contribute to the economy. Based on this research, Matloob acted as a consultant for DFID in the development of migration policy in Central Asia.
Safe sanitation
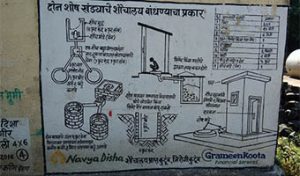 Adoption and usage of safe sanitation remains low in low-income countries. Sanitation policy across large numbers of developing countries relies on household and community adoption of safe toilets. Credit constraints and a lack of knowledge about safe sanitation have been proposed as factors constraining adoption of safe toilets. Bansi Malde is working on a project to test whether the availability of microcredit, and awareness creation activities, can boost the adoption and usage of safe sanitation in rural Maharashtra, India. The project, funded by the World Bank Strategic Impact Evaluation Fund, is in collaboration with researchers at the Institute for Fiscal Studies, a large microfinance institution, Grameen Koota and an Indian NGO, Navya Disha. Findings from the study will be disseminated to Grameen Koota, Navya Disha and policymakers, local press and key stakeholders in India in summer 2018.
Adoption and usage of safe sanitation remains low in low-income countries. Sanitation policy across large numbers of developing countries relies on household and community adoption of safe toilets. Credit constraints and a lack of knowledge about safe sanitation have been proposed as factors constraining adoption of safe toilets. Bansi Malde is working on a project to test whether the availability of microcredit, and awareness creation activities, can boost the adoption and usage of safe sanitation in rural Maharashtra, India. The project, funded by the World Bank Strategic Impact Evaluation Fund, is in collaboration with researchers at the Institute for Fiscal Studies, a large microfinance institution, Grameen Koota and an Indian NGO, Navya Disha. Findings from the study will be disseminated to Grameen Koota, Navya Disha and policymakers, local press and key stakeholders in India in summer 2018.
Scientific production
How resources should be used to accelerate scientific research and improve its quality is a central question for academic institutions and research funding bodies. In a project funded by the Leverhulme Trust, Fernanda Leite Lopez de Leon is investigating the effectiveness and benefits of academic conferences in terms of knowledge transfer, the generation of future collaborative endeavours, and academic impact, together with Ben McQuillin at the University of East Anglia. To date, findings have been published in the Economic Journal and the Journal of Human Resources, and have received coverage from the Royal Economic Society, Times Higher Education, and other media outlets. In June 2018, the School of Economics hosted a workshop on New Findings of Scientific Productivity with the participation of academic researchers and stakeholders in the area of research and innovation, to discuss findings from this project and other research in the economics of science.