Start date 1/2/2020 End date 31/7/2023
Professor Chris Farmer. Principal Investigator
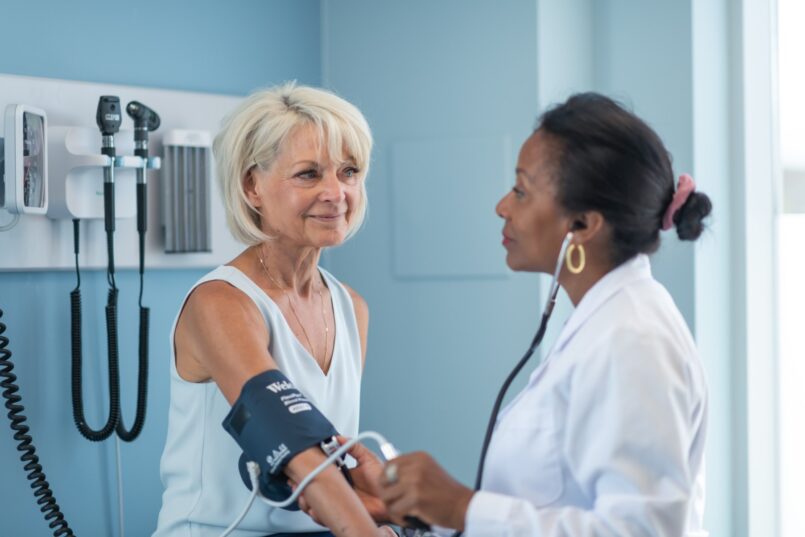
Does offering an 'at home' isometric exercise plan help NHS patients with clinically high blood pressure? – Feasibility study to assess delivery of novel isometric exercise intervention for people with Stage 1 hypertension in NHS


High blood pressure affects many people in the UK. People with raised blood pressure (140-159/90-99 mmHg) are recommended to make changes in their lifestyle (e.g. smoking/alcohol/diet/exercise) and/or medication to reduce their blood pressure. Current knowledge suggests that a particular type of exercise – isometric exercise – can lower blood pressure. Isometric exercise involves holding a fixed body position for a short period of time.
As most of the information about the benefits of this type of exercise comes from laboratory-based studies, researchers want to find out if it is possible for GP practices, and other healthcare providers, to offer NHS patients with clinically high blood pressure an isometric exercise plan to do at home and how it might affect their blood pressure over 6 months. They will also find out the experiences of those doing this type of exercise and whether it can be done consistently at home over time.
Patient and Public Involvement in this project
We have three public co-applicants on the project
Mr John Darby
Mr Alan West
Ms Anushree Biswas Sasidharan
More information on the CCCU website
Funding: NIHR Research for Patient Benefit
Who is involved
- Dr Jim Wiles, CCCU, Principal Investigator
- Dr Melanie Rees-Roberts, CHSS, Co-Investigator
- Ellie Santer, CHSS, Co-Investigator
- Dr Tim Doulton, Co-Investigator
- Dr Jamie O’Driscoll, Co-Investigator
- Dr Pauline Swift, Co-Investigator
- Public Co-Applicants (3)